Glossmeter
 Glass meter or gloss meter is used to measure the gloss of surfaces. This device emits a ray of light to the surface at a certain angle and can measure the gloss of the surface by absorbing light and calculating it according to the percentage of radiation to reflection. .
Glass meter or gloss meter is used to measure the gloss of surfaces. This device emits a ray of light to the surface at a certain angle and can measure the gloss of the surface by absorbing light and calculating it according to the percentage of radiation to reflection. .
There are several angles for measuring gloss, each depending on the type of surface. For non-metals such as coatings and plastics, the amount of light reflected at a greater angle is less, because some light rays penetrate the surface of the material and are absorbed by it or scattered in a pale form. Metals have much higher reflectivity and are therefore less dependent on angle.
Many international technical standards provide the method of use and specifications required for the application of different types of glossometers used in various materials, including paint, ceramics, paper, metals and plastics. Many industries use glossmeters in their quality control to measure the gloss of products to ensure consistency in their production processes. The automotive industry is one of the main users of the gloss meter and they use it in various applications from factory to repair shop to standardize the coating and so on.
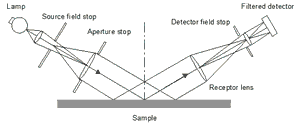
Glossmeter structure
A gloss meter typically consists of a fixed component equipped with a standard light source that reflects a beam of light to the surface and a detector with a filter suitable for receiving rays reflected from the surface and measuring on the test surface. The ASTM method states that the brightness must be defined so that the composition of the light source is spectrally corrected so that the CIE illuminates the light output, V (?) With the CIE SC light.
A variety of tools are commercially available to achieve the high standard. These tools are made using reference standards, which are usually made of highly polished, plain, black glass with a refractive index of 1.567 for the sodium D line, for which a gloss value of 100 is set for each angle.
Measure and select the angle
In order for the gauge to measure the gloss of the surface, it must be possible to measure in a small range of the overall reflection angle by measuring the transmitted and received light and the observed conditions and configuring both the light source and the viewing angle. The results of reflectometry measurements related to the amount of light reflected from a black glass standard with a refractive index are defined. The ratio of reflected light to the sample is recorded as a unit of brightness (GU) relative to the standard gloss ratio.
Measuring angle refers to the angle between the incident light and perpendicular to it. Three measuring angles (20 °, 60 ° and 85 °) are specified to cover most industrial coating applications. The angle is selected based on the predicted cutting range, as shown in the table below.
Suffering suffering |
60 ° angle |
Notes |
High gloss |
>70 GU |
If the measurement exceeds 70 GU, set the test setting to 20 ° |
Medium gloss |
10-70 GU |
|
Low gloss |
<10 GU |
If the measurement is less than 10 GU, set the test setting to 85 ° |
For example, if the measurement taken at 60 degrees is greater than 70 GU, the measuring angle should be changed to 20 degrees to optimize the measurement accuracy. There are three types of tools on the market: 60-degree angular tools, a combination of 20 and 60 degrees, and one that combines 20 degrees, 60 degrees, and 85 degrees.
Two additional angles are used for other materials. An angle of 45 degrees is specified for measuring ceramics, films, textiles and anodized aluminum, while 75 degrees is specified for paper and printed materials.
- Popular products

German laser thermometer with external thermocouple K tool 1725

Level controller / roller blade switch for solids and powders, model 1872

Industrial Laser Thermometer Instrument 1727

12-channel temperature recorder thermocouple tool 1189





















