SCADA
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition or SCADA is the most modern method of controlling, monitoring and recording information of industrial automation systems by means of a set of PLCs and DCS and intelligent sensors along with RTU stations and various industrial networks and computers. And the server is created. In SCADA systems you can have control and even logical control wherever this possibility is defined for you, even in a place outside the factory or industrial environment. Yes, this modern mechanism owes much to the most advanced advances in communication and computer science, as well as microprocessors in today's sensors.
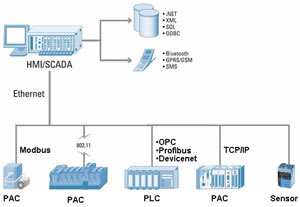
The concept of SCADA in control functions
A key feature of the SCADA system is its ability to perform monitoring work on other types of proprietary devices. The accompanying diagram is a general model that shows the application levels of production using computer control. Referring to the chart
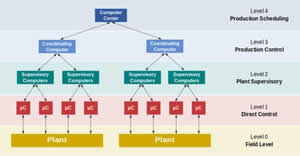
Level 1 includes programmable logic controllers ( PLCs ) or remote terminal units or remote terminals ( RTUs ).
Level 2 contains SCADA software and a computing platform. SCADA software is only available at this level of monitoring, as activities controlled by RTUs or PLCs are performed automatically. SCADA control functions are usually limited to level one monitoring or monitoring. For example, a PLC can control the flow of cooling water through part of an industrial process at a set point, but SCADA system software allows operators to change the values set for the flow. SCADAIt also allows alarm conditions or alarms such as current drop or high temperature to be displayed and recorded. The control loop is controlled directly from the RTU or PLC for feedback, but SCADA software monitors the overall performance of the loop.
Levels 3 and 4 are not traditionally in process control, but production control and planning takes place.
Data acquisition begins at the RTU or PLC level and includes the reading of instrumentation information and equipment status reporting, which is required if level 2 SCADA is required. The data is then compiled and formatted so that the control room operator uses HMI (human machine interface)Can make regulatory decisions to adjust or reject conventional RTU ( PLC ) controls . Data can also be stored as a history of performance, often based on a database management system, the possibility of process review and analytical auditing. SCADA
systems typically use a tag database that contains data elements called tags or points that correspond to the instrument or actuators in the control system based on system diagrams and instrumentation maps. Data is stored against these unique controlling process reference references.
- Popular products

German laser thermometer with external thermocouple K tool 1725

Level controller / roller blade switch for solids and powders, model 1872

Industrial Laser Thermometer Instrument 1727

12-channel temperature recorder thermocouple tool 1189





















