Solenoid Valve
Solenoid valve or solenoid valve in fluid flow control mode on and off. In most types of solenoid valves used in industry, by stimulating a coil or solenoid and moving the spool upwards, the flow or flow of gas or liquid fluid can be controlled. In practice, solenoid valves or solenoid valves are divided into different types such as diaphragm valves , needle valves with application, different pressure tolerance and of different materials ...
A wide range of solenoid valves for fluids such as steam, water, air, oil, diesel, oil, gas, etc. are used in industry, which are used as a simple method to disconnect and connect the fluid passage remotely and control its flow. . A solenoid valve is an electromagnetic device that opens or closes a fluid passage valve through a coil and passes an electric current through it, depending on the material, size, pressure, temperature, and mode of operation, as well as the number of input and output ports. Different are categorized.
Solenoid valves are used in pneumatic hydraulic applications to control jacks, etc., in automatic irrigation systems and systems, and in household applications such as washing machines, as well as in medical applications such as dental chairs.
The following is a general introduction to the types of solenoid valves in terms of performance and application
Directional solenoid valve The solenoid valves used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems are so-called directional solenoid valves. They have more than two ports for fluid inlet and outlet, while the number of positions can be more than two. With two situations and three ports that we will address in the hydraulic and pneumatic sections.
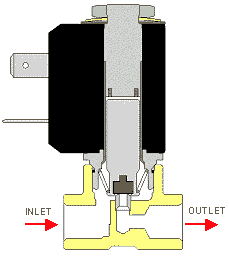
Direct-acting solenoid valve, which in this model, even with a magnetic piston, directly opens and closes the fluid path and does not require a pressure difference between the inlet and outlet, and in practice passes a small volume of fluid flow and with most fluids we've air, water, steam, oil, or any fluid compatible with the oat party or in contact with the fluid used in applications including distribution device cartridge coffee, air dryer, bath and systems, vacuum used
in The image below shows the performance of a 2/2 normal close valve directly.
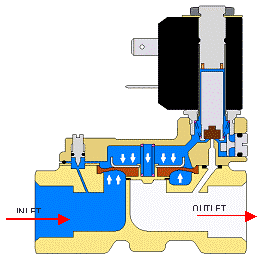
The pilot solenoid valve consists of two separate chambers separated by a diaphragm and the diaphragm is not connected to a magnetic piston that is recognizable in comparison with the direct or indirect model. It is called a pilot or indirect solenoid valve. Plain tongue uses inlet line pressure to keep the valve closed and, in practice, absorbs more of the fluid flow with less energy.
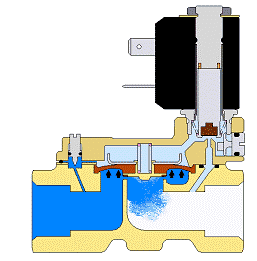
Pilot Operated with assisted lift
In this model, there is something between direct operation and pilot operation, in which the diaphragm is connected to the piston, and when the coil is excited, at low pressure, the diaphragm separates directly from the relevant part, and at higher pressures, the diaphragm is displaced by internal valve pressure. Assisted lift valves can operate at zero pressure difference, however they are not normally open. For example, this solenoid valve can be used in diesel fuel that is fed through the tank head, so that the tank pressure is not suitable to stimulate the valve in the pilot mode, and with the help of the assisted lift pilot operated solenoid valve, the diesel fuel path can be closed. Of course, it is better to use Vuitton seals for this purpose. This solenoid valve can also be used in systems with low pressure or with pressure fluctuating towards zero.
Also because these valves do not require a pressure difference to operate for vacuum or vacuum systems
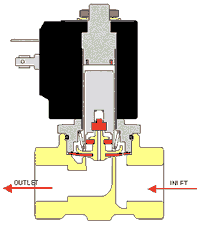
To choose the right solenoid valve, you should pay attention to the following factors:
- Maximum and minimum linear pressure at which the solenoid valve is located
- Maximum and minimum pressure difference between solenoid inlet and outlet
- Maximum and minimum flow through solenoid valve
- Specific weight, viscosity and type of fluid in terms of corrosion and ...
- Ambient and fluid temperatures
- Electrical specifications and power supply of the coil
- Explosive or non-explosive solenoid valve environment
- Popular products

German laser thermometer with external thermocouple K tool 1725

Level controller / roller blade switch for solids and powders, model 1872

Industrial Laser Thermometer Instrument 1727

12-channel temperature recorder thermocouple tool 1189





















